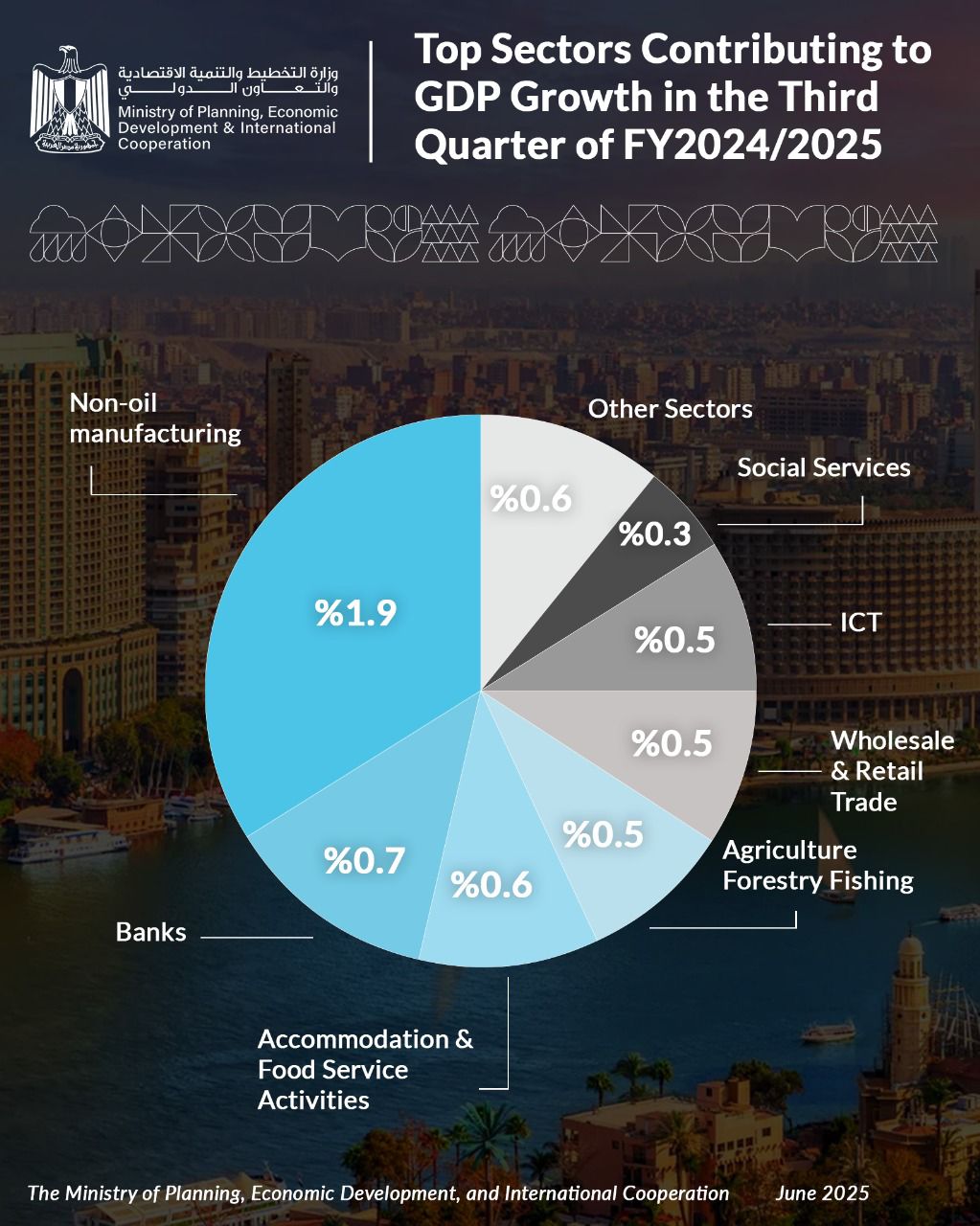
The non-petroleum manufacturing sector topped the list of sectors most contributing to the growth rates achieved during the third quarter of the current fiscal year 2024/2025, at a rate of 1.9%, according to data on the evolution of GDP growth rates for the third quarter of the current fiscal year announced by the Ministry of Planning, Economic Development and International Cooperation.
The banking sector came in second among the most contributing sectors to GDP growth, at 0.7%, followed by restaurants and hotels at 0.6%, and agriculture, forestry, and fishing, wholesale and retail trade, and communications and information technology, each contributing 0.5%.
Meanwhile, social services and construction sectors contributed 0.3% each, with other sectors (insurance, business services, electricity, real estate, and general government) contributing 0.6%.
Since the fourth quarter of the last fiscal year 2023/2024, the non-petroleum manufacturing sector has begun to achieve positive growth, shifting its contribution to growth rates from contraction to positive contribution.
The sector achieved a growth rate of 7.1% in the first quarter of the current fiscal year, then 17.7% in the second quarter, and 16.3% in the third quarter.
The continued activity in non-petroleum manufacturing reflects efforts to increase investments in the industrial sector and provide more facilities for industrial activities, aiming to shift towards tradable and exportable sectors.
This industrial growth was also linked to a significant improvement in industrial export performance, with exports of finished goods recording a 12.7% annual increase during the third quarter, enhancing the industrial sector's role as a driving force for growth.
The ready-made garments sector is a prominent example, recording an annual growth exceeding 23% during the same period, benefiting from shifts in the global trade map, which reflects the resilience of the ready-made garments sector and its ability to respond quickly to global demand.
The growth witnessed in the third quarter was evident in the continued recovery of non-petroleum manufacturing activity, achieving a growth rate of 16.03% during the third quarter of fiscal year 2024/2025 compared to the same period of the previous fiscal year, during which the activity recorded a contraction of 3.96%.
This remarkable growth in the third quarter coincides with the state's keenness to intensify investments in the industrial sector, as it is one of the priority sectors in the National Structural Reform Program.
Furthermore, the volume of Egyptian exports of semi-finished and finished goods recorded significant growth during the third quarter. Semi-finished exports (which contributed 31.9% of total merchandise exports) grew by 111.6% during the third quarter of fiscal year 2024/2025 compared to the corresponding quarter of the previous fiscal year.
Finished exports (which contributed 48.6% of total merchandise exports) also grew by 12.7%; where exports of ready-made garments, perfumes and cosmetics, various food pastes and preparations, cotton fabrics, and medicines witnessed growth of 23.7%, 21.9%, 21.5%, 9.6%, and 9.3% respectively.
Egyptian export data for ready-made garments indicate promising opportunities amidst ongoing shifts in the global trade map, as this sector witnessed a remarkable acceleration in export growth during fiscal year 2024/2025, recording an annual increase exceeding 23.7% in the third quarter compared to the same period last year. This positive performance is attributed to Egypt's benefiting from international trade tensions and importers' tendency to diversify supply sources, which reflects the flexibility of the ready-made garments sector and its ability to respond quickly to global demand.